The Role of Enterprise Governance in Value Creation
Enterprises are established with a primary objective: to create value for their stakeholders. This value creation isn't just about profit generation—it encompasses delivering quality services, ensuring customer satisfaction, and maintaining a competitive edge. This leads us to enterprise governance, or sometimes known as corporate governance. Let's explore how enterprise governance is aimed at maximising 'value' and managing the diverse expectations of corporate stakeholders.
Understanding Value in Enterprise Governance
In the context of enterprise governance, 'value' is a broad concept that extends beyond mere financial gains. When discussing value the following concepts have to be put into consideration:
Revenue Generation: The basic measure of business success, focusing on profitability and growth metrics.
Quality Services: Commitment to high standards in product and service delivery, which in turn boosts customer loyalty and market reputation.
Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring that the needs and expectations of customers are met, thereby increasing retention and attracting new clients through positive word-of-mouth.
Competitive Edge: Staying ahead of industry trends and innovations to outperform competitors and capture more market share.
However, the challenge in creating value lies not simply in achieving these benefits. A key part in turning these benefits into value is the proper resource management. This involves optimizing costs, leveraging assets effectively, and making strategic decisions that balance immediate needs with long-term goals. Without wise resource management, the cost of the above listed concepts can quickly grow bigger than the benefits they bring to the organization.
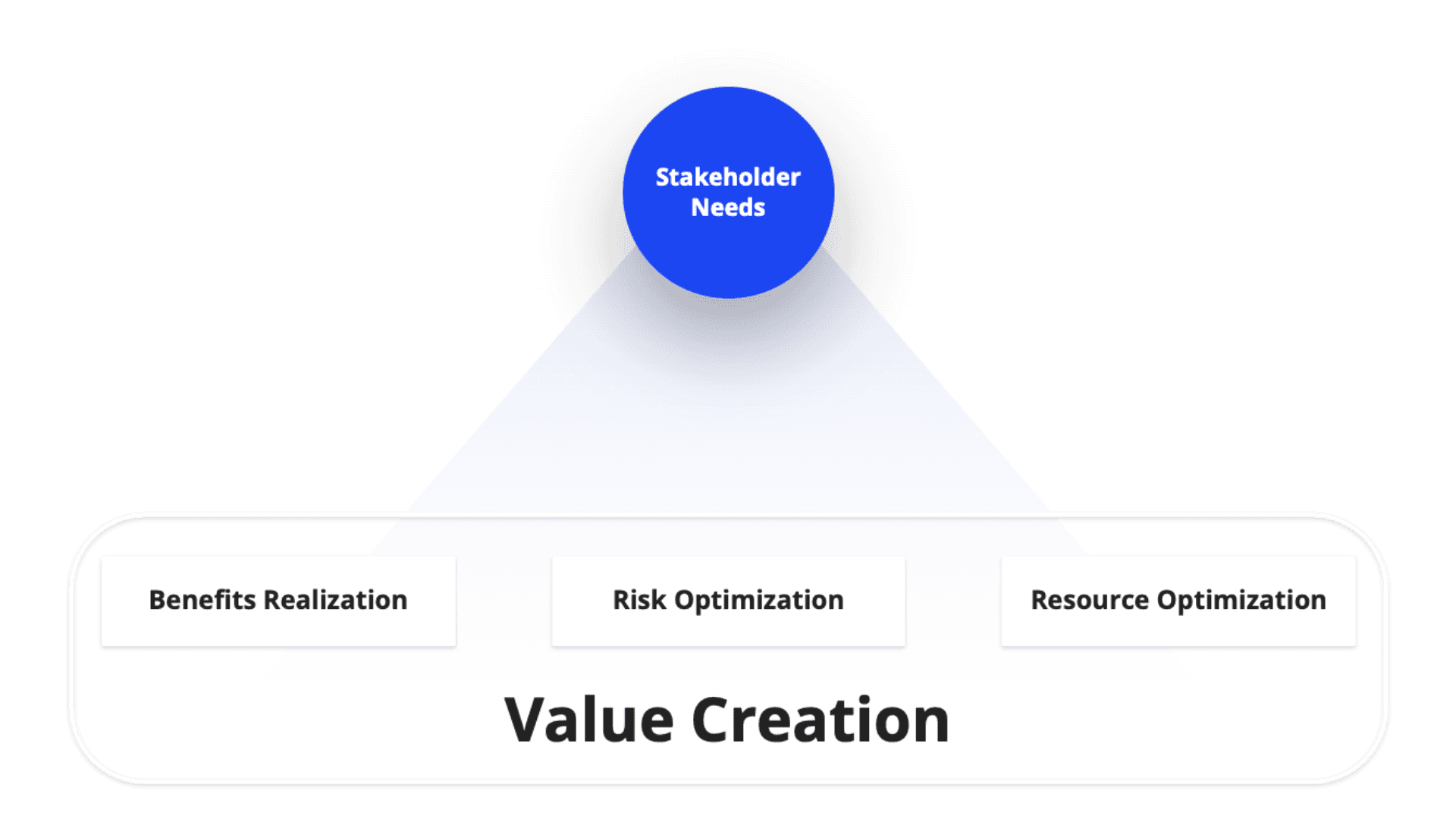
Stakeholder Needs
Stakeholders in an enterprise range from investors and customers to employees and suppliers, each with their unique expectations of what 'value' means. Investors might prioritize financial returns, while customers look for quality and reliability. Employees seek fair compensation and a positive work environment, and suppliers desire consistent demand and prompt payments.
This diversity of expectations can lead to potentially conflicting goals and priorities within an enterprise. Herein lies a critical role of governance: to mediate these differences and translate disparate needs into a cohesive strategic direction for the company. Effective governance mechanisms ensure that these interests are balanced in a way that supports sustainable business growth.
Let's have a look at key components of effective enterprise governance:
Strategic Alignment: Ensuring that all business operations and decisions align with the overarching strategic goals of the enterprise.
Accountability: Establishing clear lines of responsibility and accountability across all levels of the organization.
Transparency: Providing stakeholders with clear and accurate information about the company's operations and performance.
Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impede the organization’s ability to create value.
Ethical Standards: Upholding high ethical standards to foster trust and integrity in all business dealings.
Challenges in Enterprise Governance
Implementing an effective governance framework is not without challenges.
Organizations must navigate:
Complex Regulatory Landscapes
Each jurisdiction can have a significant number of laws and regulations in place. Keeping up with in laws and regulations across several different jurisdictions can be daunting. Especially, since these laws and regulations are not set in stone – all relevant changes must be monitored, and the governance framework must be adjusted according to these changes if needed.
Cultural Barriers
Global organizations often face challenges in implementing uniform governance practices across diverse cultural landscapes. That is because people from different cultures can have very different beliefs about leadership, teamwork or decision-making. Implementing new governance policies can therefore cause employees to feel alienated and resist the changes, if they feel these changes don’t align with their own cultural norms.
Technological Changes
Rapid technological advancements can outpace existing governance frameworks, requiring continual updates and adaptations. However, new technology for its own sake is not an option, the cost of new technologies and whether they are truly worth the investment must always be considered. Another thing to keep in mind is the potential skill gap between employees – not all of them have the needed know-how to work with new technologies, which can lead to inefficiencies in governance processes.
This demonstrates that enterprise governance is crucial for guiding organizations toward sustainable value creation. It achieves this by establishing a framework that balances diverse stakeholder interests with the organization’s overall objectives. When implemented effectively, it enables organizations to navigate the challenges of operating across different jurisdictions and cultures, enhancing their chances of thriving in competitive and rapidly evolving business environments.




