Welcome to LearnGRC, a weekly newsletter where I provide actionable advice to help you launch, grow and accelerate your career in Governance, Risk and Compliance.
There is a lot of confusing when it comes to certifying a management system. In the following article, you will learn how to undergo an external ISO/IEC 27001 certification audit and how to maintain it over the course of a 3-year cycle.
The ISO 27001 Certification Process
Once you have implemented the standard and the results of the internal audit programme, as well as the outcome management review have given you a great feeling, you are ready to tackle the certification audit. Achieving ISO 27001 certification is a structured process, designed to ensure an organization's information security management system (ISMS) is comprehensive and effective. It is broken down into the following five steps:

Step 1: Selecting a Certification Body
The first step is to choose a reputable certification body. This is crucial as they are responsible for conducting the certification audits. Organizations should reach out to various bodies to compare proposals, fees, and terms before committing.
Step 2: Documentation Review
The certification body begins with a documentation review to understand the organization's ISMS. This includes assessing the Statement of Applicability and mandatory documents. Some organizations opt for a pre-audit by independent auditors to prepare for this step, although it's not a requirement.
Step 3: Stage 1 Audit
The stage 1 audit is a preliminary audit where the auditor familiarizes themselves with the organization's policies and procedures. They identify any significant gaps or nonconformities that need addressing before the more detailed stage 2 audit.
Step 4: Stage 2 Audit
In the stage 2 audit, the certification body conducts a comprehensive review of the ISMS, covering all processes and controls. If major nonconformities are found, the organization has up to 90 days to address these issues. The successful completion of this audit leads to the issuance of the ISO 27001 certification by the national accreditation body.
Step 5: Maintaining Certification
The final step involves maintaining the certification over a three-year period with annual surveillance audits. These audits verify the ongoing effectiveness of the ISMS. At the end of the three years, a re-certification audit is required to renew the certificate for another cycle.
How to maintain a Certification
Post-certification, the timeline for maintaining ISO 27001 compliance is structured into annual segments, each with specific objectives to ensure the ISMS remains effective and responsive to new challenges.
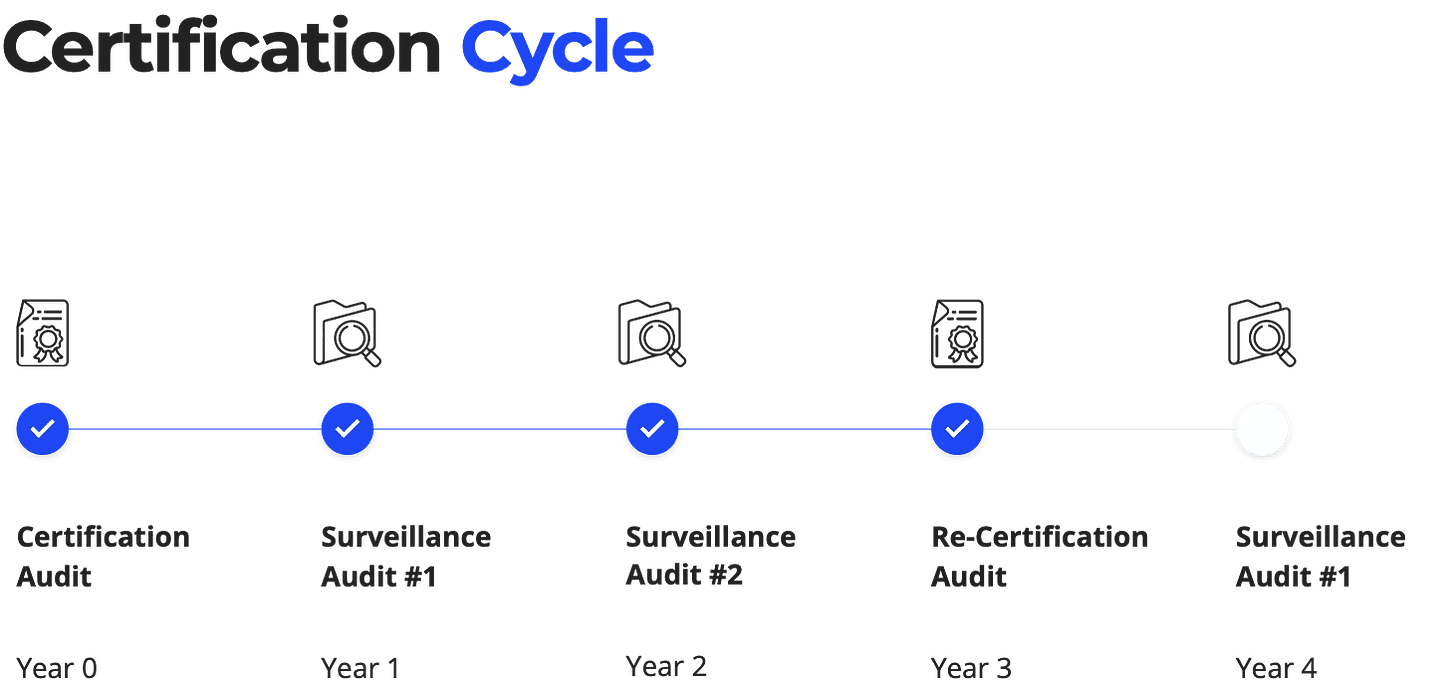
Year 0: Certification Audit
The moment the certification audit is successfully completed, an organization's ISMS is officially recognized as compliant with ISO 27001 standards. This milestone marks the commencement of a three-year certification cycle, with the certification audit setting the benchmark for the organization's information security practices.
Year 1: First Surveillance Audit
Months 1-6: Focus on internal audits and management reviews to refine the ISMS, ensure the closing of any gaps identified during the certification audit, and implement continuous improvement measures.
Months 7-9: Begin preparations for the surveillance audit by reviewing areas of the ISMS that will be the focus of the upcoming audit, based on previous findings or critical areas of the business.
Months 10-12: Conduct the first surveillance audit, which assesses select components of the ISMS to ensure continued compliance and effectiveness. Any identified nonconformities must be addressed promptly to avoid impacting the certification status.
Year 2: Second Surveillance Audit
Months 13-18: Continue the cycle of internal audits and reviews. Update policies and procedures as necessary to reflect changes in the organization or external environment.
Months 19-21: Prepare for the second surveillance audit by focusing on areas due for review and any new or revised aspects of the ISMS.
Months 22-24: The second surveillance audit takes place, with the same goals as the first year—to verify the ongoing effectiveness of the ISMS and to rectify any nonconformities.
Year 3: Recertification Audit
Months 25-30: This period should be used to conduct a comprehensive review of the entire ISMS, re-evaluate risk assessments, and ensure that all earlier nonconformities have been satisfactorily addressed.
Months 31-33: Intensify preparations for the recertification audit by conducting thorough internal audits and ensuring that all employees are up-to-date with their training and aware of their roles within the ISMS.
Months 34-36: The recertification audit is carried out to examine the full ISMS, similar to the initial certification audit. Successful completion will renew the ISO 27001 certificate for another three years.
Throughout this timeline, organizations must maintain a proactive stance on information security, regularly updating their ISMS in response to new threats, technological advances, and business changes. The certification cycle is designed not just to assess, but also to drive improvement, ensuring that an organization's information security measures are always at the forefront of best practices.